Graph database
Ref: https://www.graphable.ai/blog/what-is-a-graph-database/
- Graph databases store data in form of graphs.
- Leveraged in use cases that are particularly focused on connectedness within data.
- The connections in a graph db data are as important as the data itself.
Example - consider the following tabular data:
Name Job Address Sonya Pilot 101 N Main St Parker Food Service 101 N Main St Alex Pilot 455 West Ave This table is quite efficient in answering queries like “Where does Sonya live?” as it can be done via a simple lookup. On the other hand, if we were to ask a question like “Who also lives at the same place as Sonya?” which is inherently interconnected, then this requires multiple lookups on the table. In this example, we would have to do a lookup to get Sonya’s address and then another lookup to get all people with that same address. Such queries can easily get out-of-hand on larger more complex data.
To perform the same operation on data stored as a graph, we extract all distinct entities in the data and treat them as nodes. This can require an entire entity resolution process depending on how structured/complex the data is. After extracting unique entities, we create relationship edges between any nodes which share a connection to that record by specifying the type of relationship between the nodes. This allows storing the fact that two entities are related along with how they are related. For the above example, this can look like
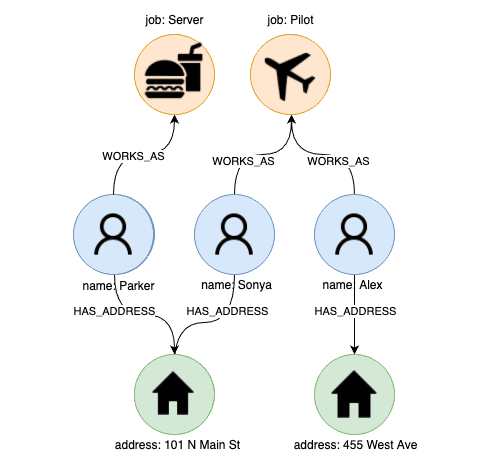
Figure 1: Source: https://www.graphable.ai/blog/what-is-a-graph-database/ Now, to answer the question being discussed, we start by locating the entity in question (Sonya) -> find their address (traversing via the HASADDRESS relationship) -> Follow all other HASADDRESS relationship on that node to find adjacent datapoints.
Such queries can be very efficiently executed using GraphQL (Cypher, Gremlin etc.)
- Can’t these things be done in RDBMS?
- Yes, but for each relationship extra time/compute needs to be spent to calculate the value of the relationship but graphDB stores it inherently.